industrial 3d printer manufacturer
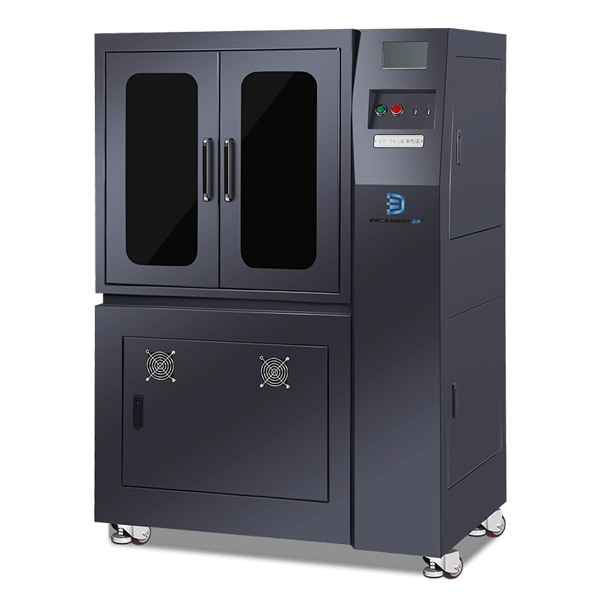
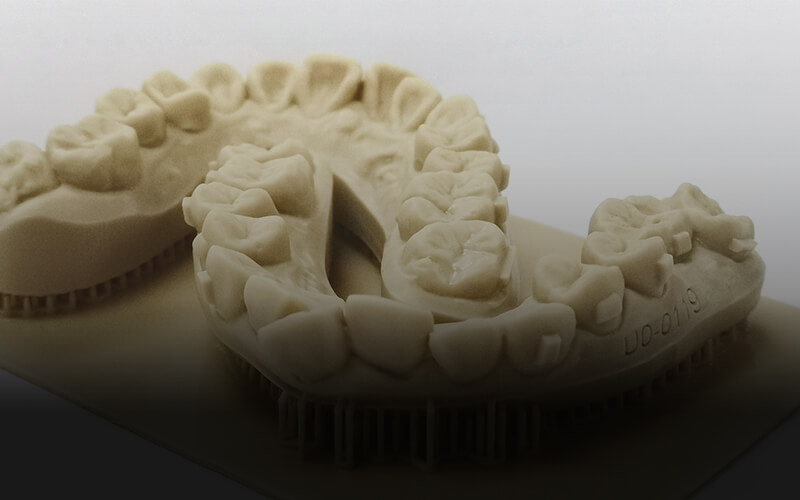
Dreambot3D is an industrial 3D printer manufacturer that produces FDM and LCD 3D printers. Our 3D printers are suitable for high quality 3D printing in industries such as: jewelry, aerospace, automobile, medical, dental, handicraft, toymaking industries, etc.
We produce different models and sizes of the 3D printer for commercial and personal applications.
Dreambot3D 3D printers for your Choice
FDM 3D Printers

The L-300 printer prints at a speed of 20 to 150mm and printing size of 300x300x300mm.
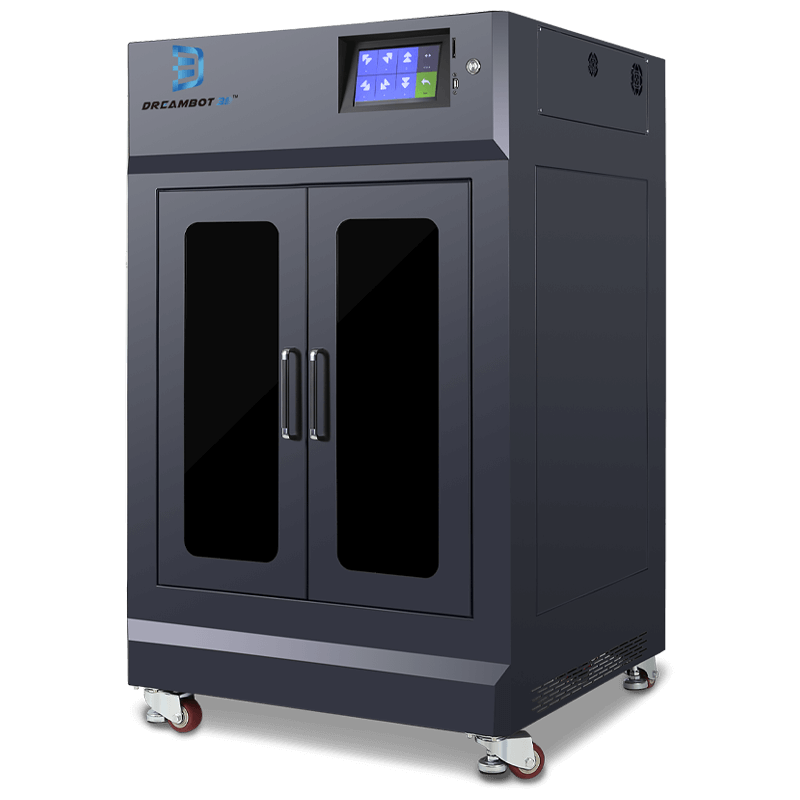

The L-400 printer prints at a speed of 20 to 150mm with a printing size of 400x400x400mm.
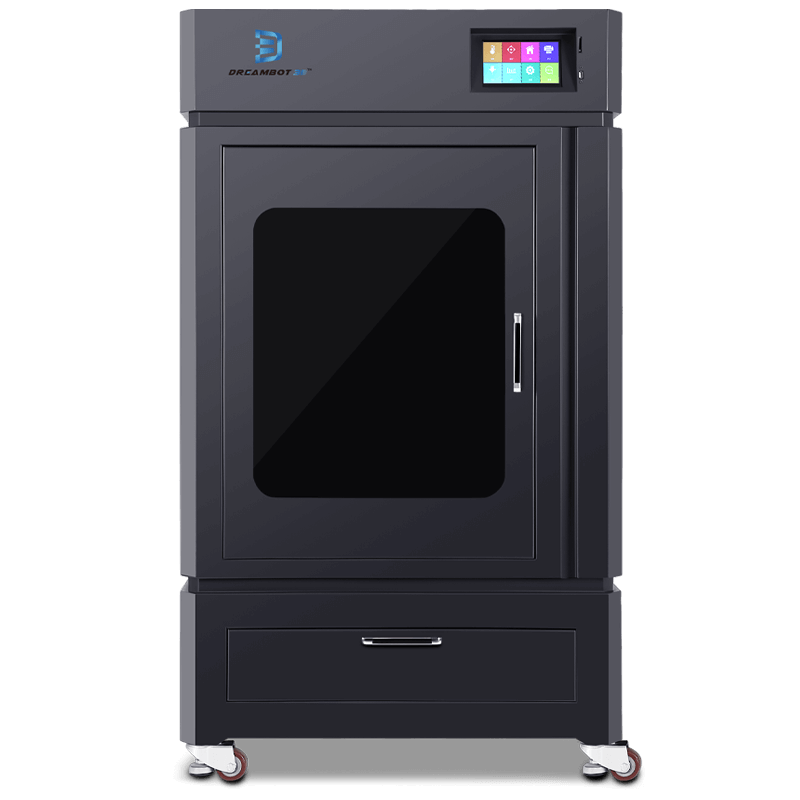

The L-500 printer prints at a speed of 20 to 150mm with a printing size of 500x500x500mm.
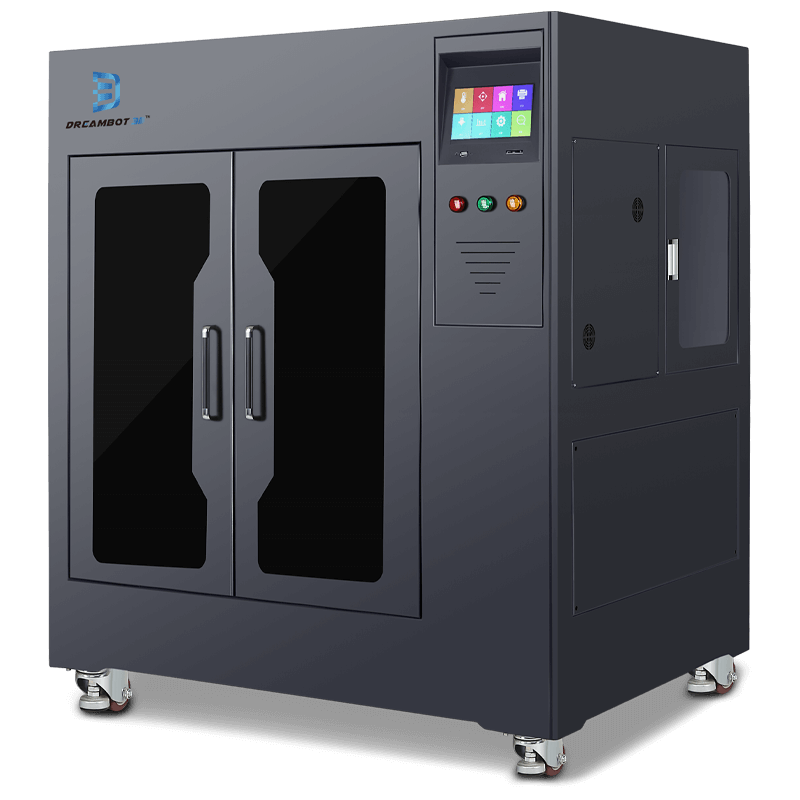

The L-600 printer prints a layer thickness of 0.05 to 0.3mm and 600x600x600mm size.
The L-600 printer prints a layer thickness of 0.05 to 0.3mm and 800x800x800mm size.
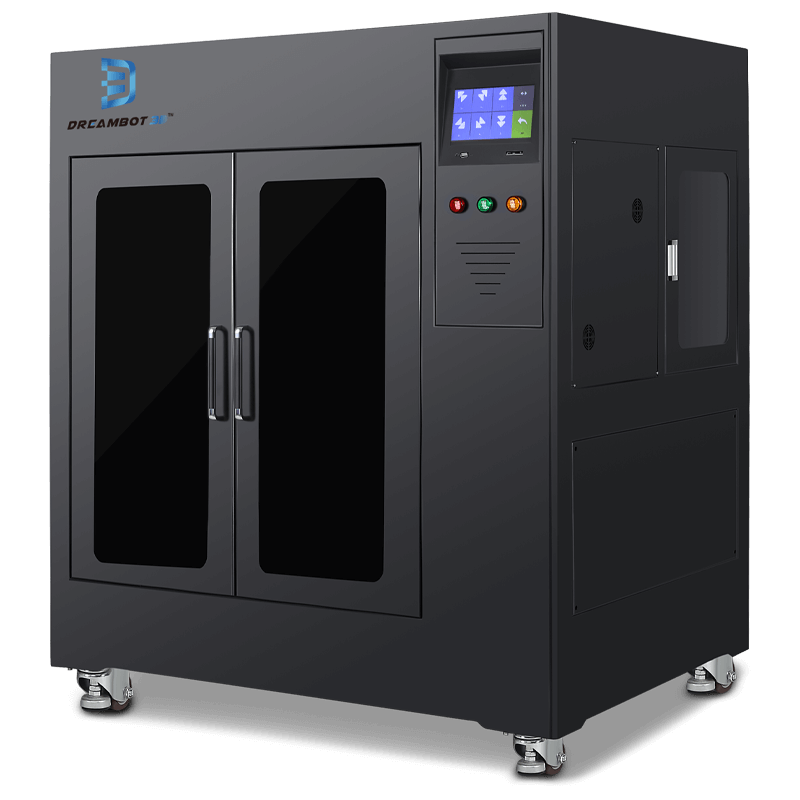

The L-1000 printer prints a layer thickness of 0.05 to 0.3mm and 1000x1000x1000mm size.
LCD 3D Printers

The ME-192 LCD printer has a printing accuracy of 0.025 to 0.1mm.
The ME-215 LCD printer has a printing accuracy of 0.03 to 0.1mm.
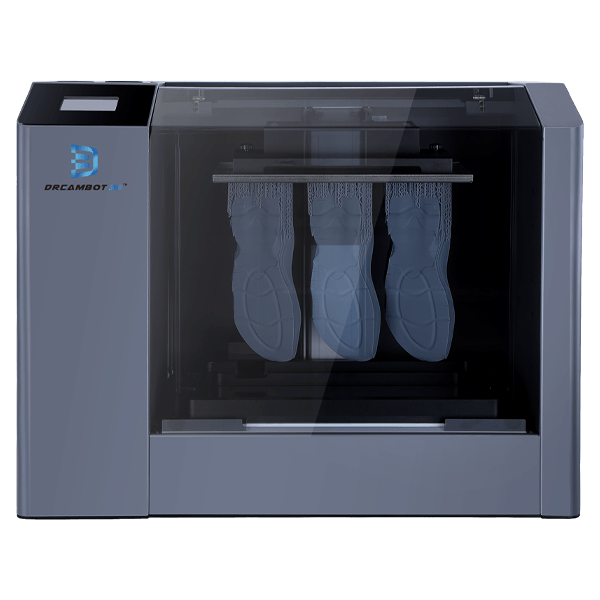

The ME-345 LCD printer has a printing accuracy of 0.02 to 0.15mm.
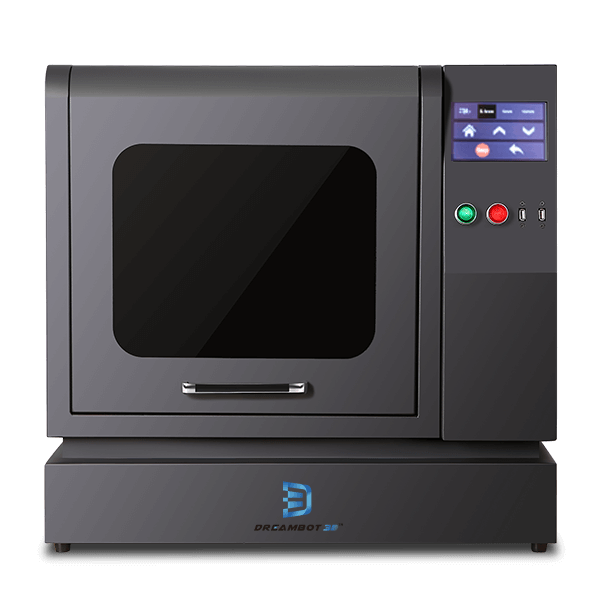

The DB-345 LCD printer has a printing accuracy of 0.025 to 0.1mm
Contact Us
industrial 3d printer manufacturer
At Dreambot3D, we are industrial 3D printer manufacturers that provide high quality 3D printing technology. Our 3D printers are affordable with distinct features such as heated glass bed, large build volumes, high printing accuracy, easy to use interface, etc.
Our printers are perfect for different sizes of 3D printing suitable for commercial applications and for hobbyists.
The 3D printer cost is affordable and the cost of operating is not demanding for production.

CE FCC ROSH approved

Solution for 3d printing

High quality
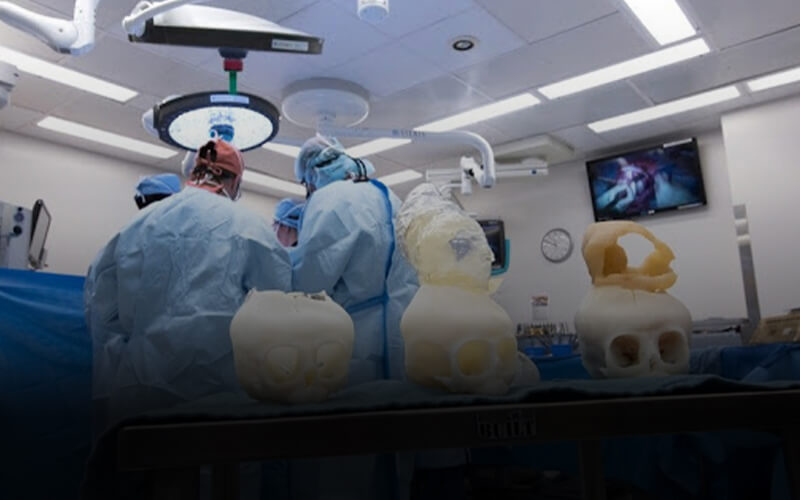
Application of industrial 3D printers
I need a Printing solution
Our technical team will provide you with a custom 3d printer solutions you need.
What Our Customers Say
Industrial 3D Printer Buying Guide
Introduction of 3D Printers on the Market
3D printing is now a household term across numerous parts of the world. From engineering to education, automotive to aerospace, 3D printing equipment runs rampant.
Having a 3D printer at home or in your production line heightens productivity to an inestimable extent. 3D printing equipment facilitates easy design, structuring and modelling of different materials.
There multiple variants of 3D printing equipment available, each is operating with a unique principle and suitable for printing specific material. This buying guide is optimised to help you understand all the intricacies, challenges and opportunities attached to purchasing a 3D printing equipment.
From the different variants available to the printing style and the most suitable 3D printing equipment for every production line, we covered it all.
If you are looking to venture into the opportunities 3D printing technology is offering on a mainstream level, we recommend you take out time to explore this guide.
1.1, What are the 3D printers with different principles?
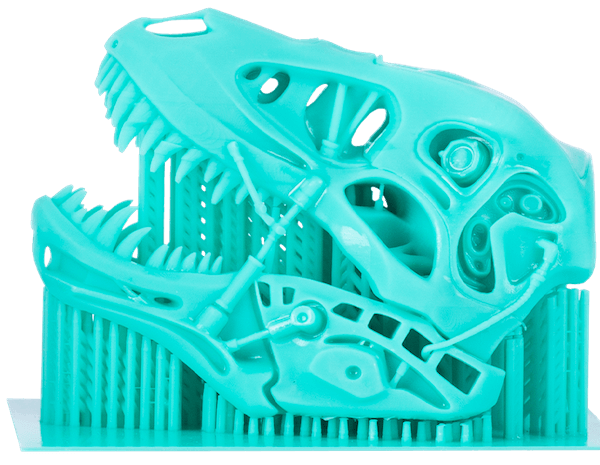
To begin, let’s start with the basics. What is 3D printing? 3D printing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. These printing equipment are suitable for designing mannequin, animations, biocompatible materials, electrical prototypes, medical equipment etc.
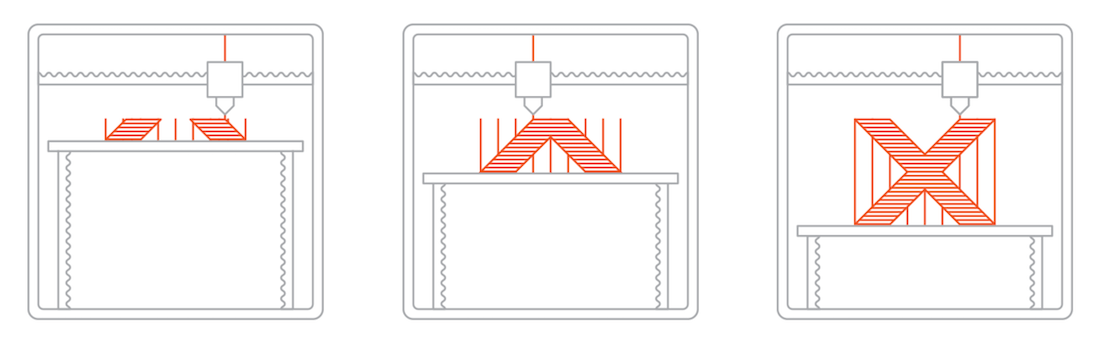
While 3D printing equipment is available and accessible by everyone, the buying process is quite complex due to the variants available. To obtain a formidable 3D printer for your printing needs, you need to understand the underlying principle behind most of the variants available—the section details out the working principle of the four major 3D printers.
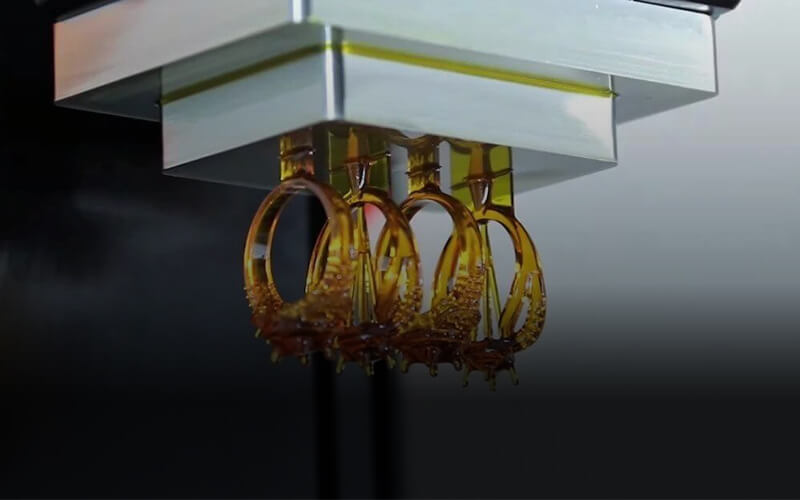
Liquid Crystal Display {LCD}: Liquid crystal display printers or LCD printers as they are popularly known are industrial 3D printers use to create 3D models or designs of numerous objects in education, automotive, aerospace, medicine, dentistry etc.
LCD printing equipment generates their light source through an array of UV LCDs. These printers are used to create 3D patterns or images of CAD models using materials such as resin, wax or metals. The images or 3D models obtained using LCD 3D printers are composed of dots.
LCD 3D printing equipment display image by sending light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters. This dichroic filter separates light into three polysilicon panels. In simple terms, a liquid 3D printer uses an array of UV LCD as its light source. The printer shines light directly from the flat LCD panel in a parallel fashion onto the build area.
As the light travels through the light source, the individual pixels open up to allow light to pass or close to block the light. This combination of open and closed pixels creates room for the liquid polymer 3D printer to produce multiple colours and shades on the projected image.
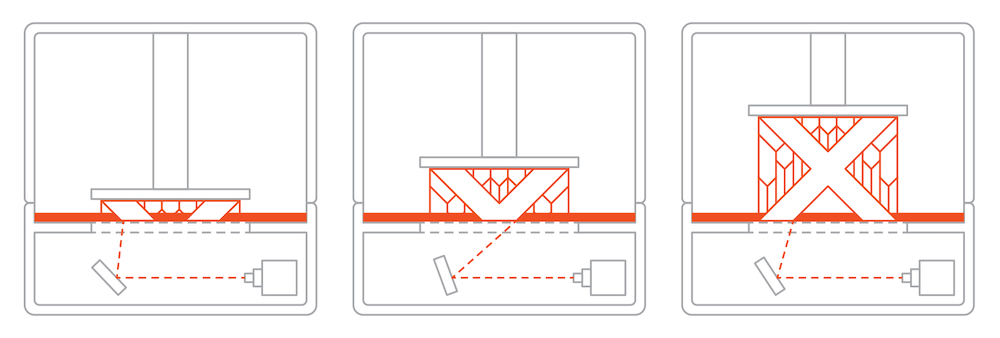
The light emitted from an LCD 3D printer isn’t expanded—that’s, it doesn’t spread beyond its projected frame. When using these 3D printers, you can design patterns and images of multiple variations; rest assured you wouldn’t experience pixel distortion halfway. Note that unlike most other resin printers, the LCD 3D printing equipment print quality depends on its LCD density.
Fused Deposition Modelling {FDM}: FDM 3D printing equipment is currently the most popular 3D printing technology. FDM printing was originally developed and implemented by Scott Crump from Stratasys, founded, in the 1980s.
Other 3D printing companies have embraced similar technology but under different names. A well-known manufacturer MakerBot coined a virtually identical technology, calling it Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF).
Industrial 3D printers use FDM Technology to construct objects layer by layer from the very bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament. The whole process is somewhat similar to stereolithography. Specialized programs or Slicers “cut” CAD models into layers and computes the manner printer’s extruder would assemble each layer.
In addition to thermoplastic, a printer may extrude support materials too. Then the printer heats thermoplastic until its melting point and extrudes it throughout nozzle on a printing bed, which you may know as a build platform or a desk, on a predetermined pattern determined by the 3D model and Slicer software.
Digital light processing {DLP}: DLP is another industrial 3D printer quite much like stereolithography. The DLP technology was made in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments and became well known for its use in the production of projectors.
It utilizes digital micromirrors laid out on a semiconductor chip. The technology is found in mobile phones, film projectors, and, of course, in 3D printing. For 3D printing, both DLP and SLA functions with photopolymers. However, the difference between SLA and DLP 3D printing equipment is that DLA requires an additional source of lighting.
3D printing amateurs frequently use more traditional sources of lights like arc lamps for DLP printing. The other important piece of the DLP puzzle is an LCD (liquid crystal display) panel, which gets applied to the entire surface of the 3D printed layer during a single run of the DLP procedure.
The substance used for printing is a liquid plastic resin that’s set in a transparent resin container. The resin hardens quickly when exposed to a lot of photons, or more simply put, bright light.
The printing speed for DLP 3D printing equipment is the kicker. A layer of hardened material can be produced with this kind of printer in a few seconds. After the layer is completed, it is transferred, and printing of the next layer is started.
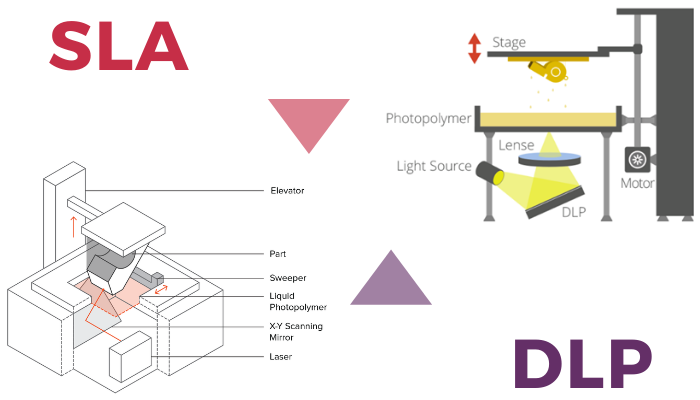
Stereolithography SLA: SLA is a 3D printing equipment which could be used to execute your projects that involve the 3D printing of items. Although this process is the earliest one in the history of 3D printing, it is still in use today.
The idea and application of this method are amazing. Whether you’re a mechanical engineer, who wants to confirm whether the part can fit your design or creative individual who wishes to print a plastic prototype for a fresh upcoming project, Stereolithography 3D printing systems can truly bring your 3D models to life.
SLA industrial 3D printers do not function like normal desktop printers that extrude some quantity of ink to the surface. SLA 3D printers operate with an excess of liquid plastic that after a while hardens and forms to a solid object.
Note that parts printed by stereolithography 3D printers usually have smooth surfaces, but its quality depends on the quality of SLA printing equipment used.
After the plastic hardens a stage of the printer drops down in the tank, a fraction of a millimetre and laser forms another layer until printing is finished. After all, layers are printed, the item has to be rinsed using a solvent and then put in an ultraviolet oven to complete processing.
The time required to print an object depends upon the size of the SLA 3d printing system utilized. Small items can be printed within 6-8 hours using a basic kid’s 3D printer, while large 3d prints can be several meters in 3 dimensions and printing time could be up to several days long.
1.2, Why FDM and LCD are the main Productivity Tools in the Current 3D Market
With the information above, we believe we now have a common understanding of how the different types of 3D printing equipment available operate. The four 3D printing equipment we listed out are the most commonly used worldwide. They all possess exceptional features that can help you enjoy a smooth and reliable printing process.
However, in terms of durability, efficiency and cost, LCD resin 3D printers and industrial FDM 3D printers are the most viable. They are known as the powerhouse behind most hundreds of highly sophisticated production lines.
It wouldn’t come as a surprise if you are wondering why industrial FDM 3D printers and LCD resin 3D printers are highly valued and placed far ahead of the rest—it’s a highly welcomed thought.
To help you further understand why it’s essential you build your production line around LCD or FDM 3D printing equipment or if possible both, let’s have a look at their basic differences based on the application area, working principles and compatible material.
1.2.1, Material Difference Between LCD and FDM printers.
LCD resin 3D printers are industrial 3D printers that use plastic resin as the raw material, in contrast to the filament used in FDM technology.
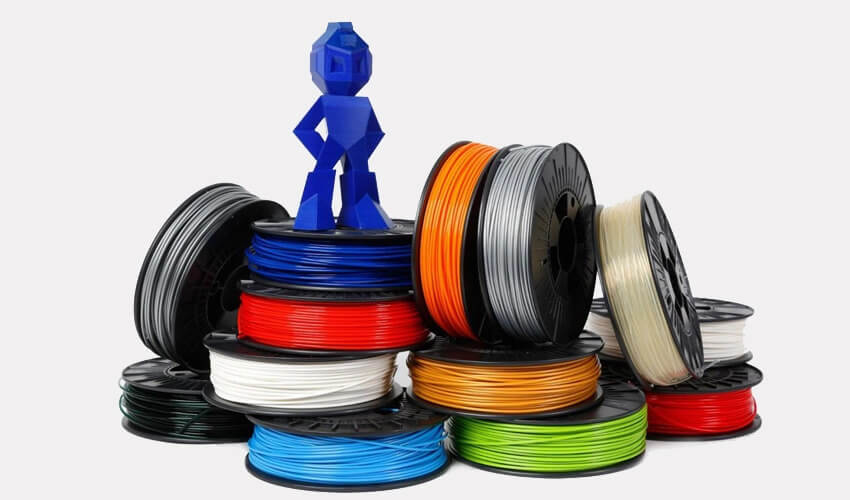

The liquid resin used in LCD 3D printing is typically composed of either epoxy or a combination of acrylic and methacrylic monomers. When exposed to UV radiation, these monomers quickly form molecular bonds with each other and turn into a solid polymer.
Thermoplastic materials stand as the most viable printing material for industrial FMD 3D printers. Thermoplastic materials are preferred because of the malleable nature they possess when heated. This remarkable feature gives room for each layer to stick together during the creation process.
1.2,2, The Principle Difference Between FDM and LCD
The durability industrial FMD 3D printers and LCD 3D resin printers provide us not just based on material alone. The working principle behind both 3D printing equipment also goes a long way to determining how formidable or irrelevant your printing operation would be.
To further demystify the printing process involved, lest look at the working principle behind LCD resin 3D printers and industrial FDM 3D printers.
LCD resin 3D printers typically display images by sending light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters that separates light into three polysilicon panels. In simple terms, a liquid 3D printer uses an array of UV LCD as its light source. The 3D printing system shines light directly from the flat LCD panel in a parallel fashion onto the build area.
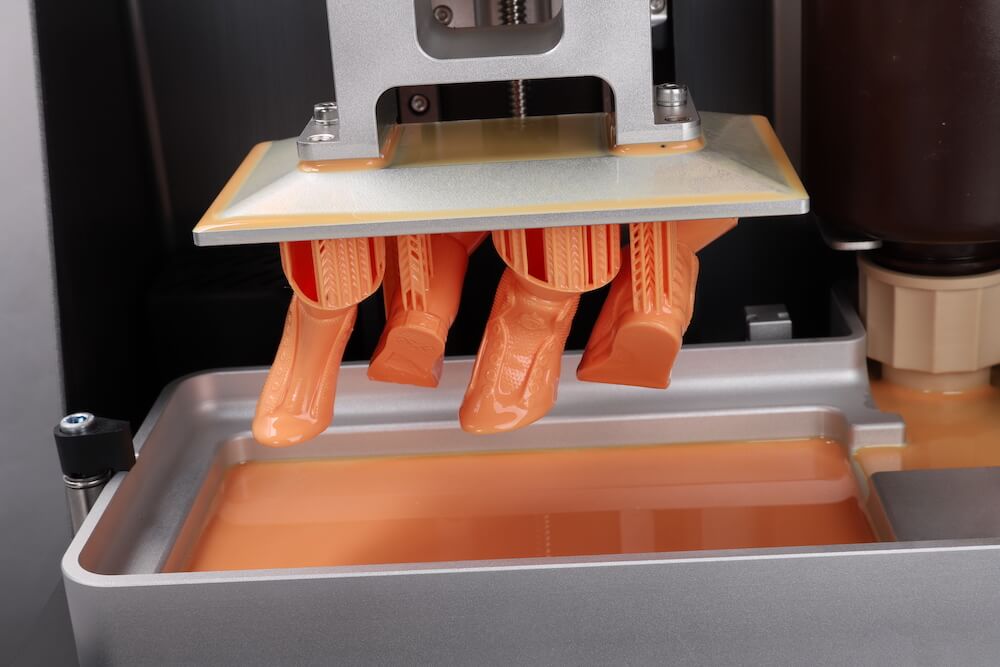
As the light travels through the light source, the individual pixels open up to allow light to pass or close to block the light. This combination of open and closed pixels creates room for the liquid polymer 3D printer to produce multiple colours and shades on the projected image.
The light emitted from an LCD 3D printer isn’t expanded—that’s, it doesn’t spread beyond its projected frame. When using these 3D printers, you can design patterns and images of multiple variations; rest assured you wouldn’t experience pixel distortion halfway.
On the other hand,
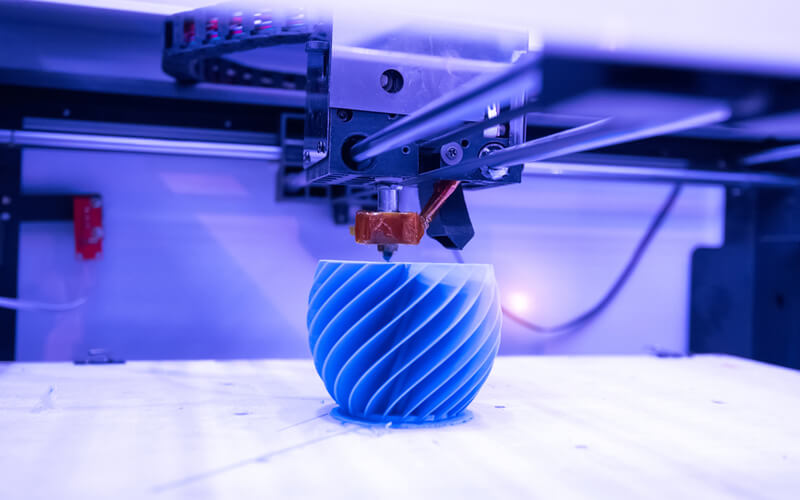
For an industrial FDM 3D printer to function properly, it requires a heated nozzle, a build platform, and raw material to build upon. The printing process begins after the modelling software slices the 3D CAD file creating an extrusion path for the nozzle to follow.
All necessary support needed by the object is factored into the extrusion path, and the nozzle movement is controlled via the interactive interface found on the machine.
When the software successfully determines a suitable path for the nozzle, the filament is let loosed and fed through the heated nozzle. As soon as the raw material gets to the nozzle, it dissolves to a semi-liquid state and is forced out of the nozzle in the form of super fine beads. Immediately after the material leaves the nozzle, it hardens and bonds to the layer under it.
Using the FMD machine’s mechanical interface, you can lower the platform holding the material to about one-sixteenth of an inch, giving room for the nozzle to start working on the next layer. Note that to remove the object or model created from the platform, you have to either break them off or use a solution of detergent and water.
1.2.3, The Difference Between FDM and LCD in the Application Area
Industrial FDM 3D printers and LCD resin 3D printers possess similar characteristics in terms of application area. While the type of materials these printers use in creating 3D models are quite different, they can both serve as sustainable 3D printing equipment for creating models and patterns in similar industries.
However, this section is focused on helping you sight the basic differences between FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment and why they are regarded as formidable productivity tools by experts in numerous industries.
1.2.4, Application Field of LCD Resin 3D Printers
Jewelry: since the inception of LCD 3D resin printing methods, the workflow and customization process has changed. Almost every jeweler now offers customizable options with unique designs. LCD 3D printing equipment did not only make the jewelry mold creation process fast and accessible; it also made it cheap and affordable.

Medicine: LCD 3D printers are amongst the few resin 3D machines pioneering remarkable development in the dental industry. LCD 3D printing equipment design process is not just optimized to create 3D resins of biocompatible materials used for dental procedures; it is also structured to maintain a specific level of precision and accuracy that can be seconded to none.
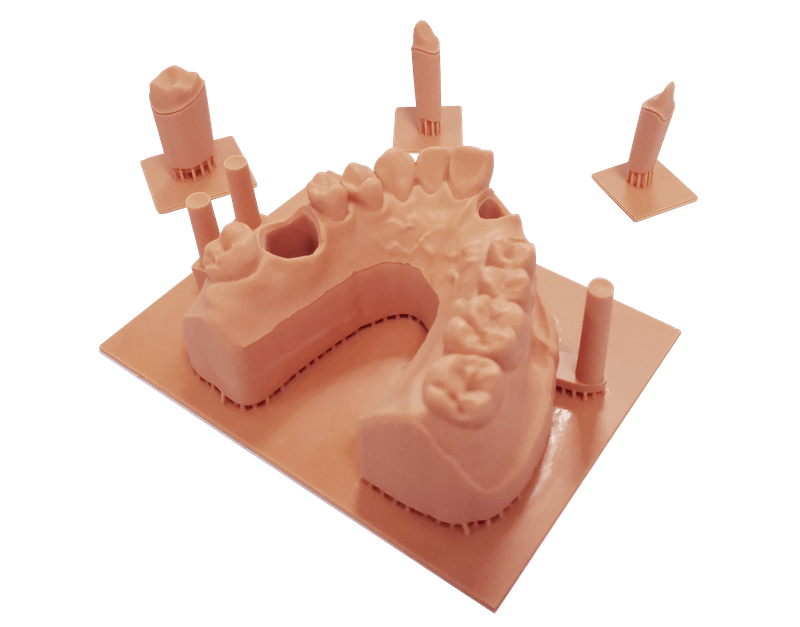
Research and Development: Keeping up with customers’ constant demands, challenging competition, and varying customer needs requires materials and resources that can easily adapt to structural or categorical change.
LCD resin 3D printers help streamline an iterative process that keeps the production line on a constantly evolving front to meet its customers’ dynamic needs. With a 3D printed model to direct the workflow, individuals in the R&D team can enjoy a fast and efficient prototyping process.
Education: complexity can be demystified and practically broken-down from the four walls of a brick-and-mortar class—3D printing equipment create room for a structural understanding of multiple designs. LCD resin 3D printers are widely used in numerous educational institutions around the globe.
Model Making: 3D printings provide a real-time representation of an expected outcome. From fashion to tech, medicine to education, its usage is enjoying remarkable dominance. LCD 3D printers are the leading resin 3D printing machine for designing models flexible enough to meet dynamic needs.
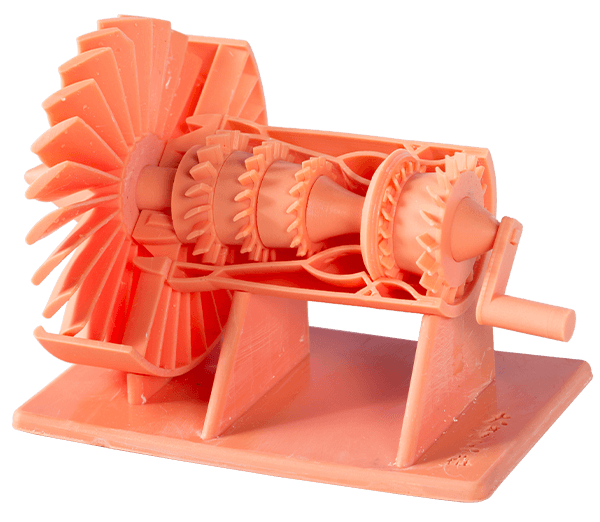
LCD 3D printers come in different type, size, and range; you can explore our collection to get detailed info on an LCD resin 3D printer suitable for the task at hand.
1.2.5, Application Area for Industrial FDM 3D Printers
Model Making: Just like LCD 3D printers, industrial FDM machines are also suitable for creating exceptional models. FDM 3D printing equipment is amongst the few built to sustainably cater to all your printing needs at a low cost.
The printing machine is simple to use and easy to set up. Purchasing an industrial FDM 3D printer from our catalog would enable you to enjoy a smooth and efficient 3D printing process right out of the box.
![]()
Industrial Research and Development: Having a professional FDM 3D printing equipment when carrying out a research and development task can help you highlight potential risk areas early on. Industrial FDM 3D printer allows you to prototype and tests small components within a limited time quickly.
The machine helps designers access design frameworks and operation sequence conventional R&D processes doesn’t leave much room for.
Production of Animation Figures: Industrial FDM 3D printers are regarded as a durable option for creating animations because it grants designers the opportunity to pay meticulous attention to detail while leaving room for even the most minor editing to be carried out. With the best FDM printing equipment at your disposal, you can streamline an animation creation process; rest assured, accuracy is guaranteed.
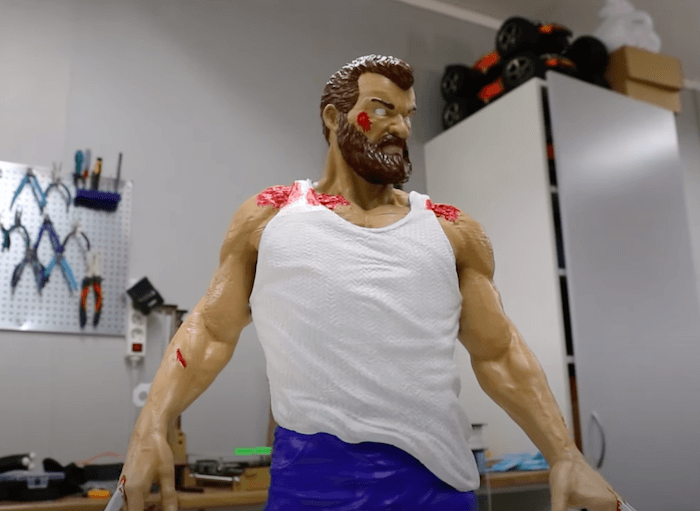

Aerospace and Automotive: industrial FDM 3D printers brought about massive improvements in design, validation, production, and customization. Industrial 3D printer companies impact in the aerospace and automotive industry doesn’t just revolve around the research and development phase—designs and patterns created using FDM 3D printing equipment stand as the bedrock powering the day to day innovations of the aerospace and automotive industry.
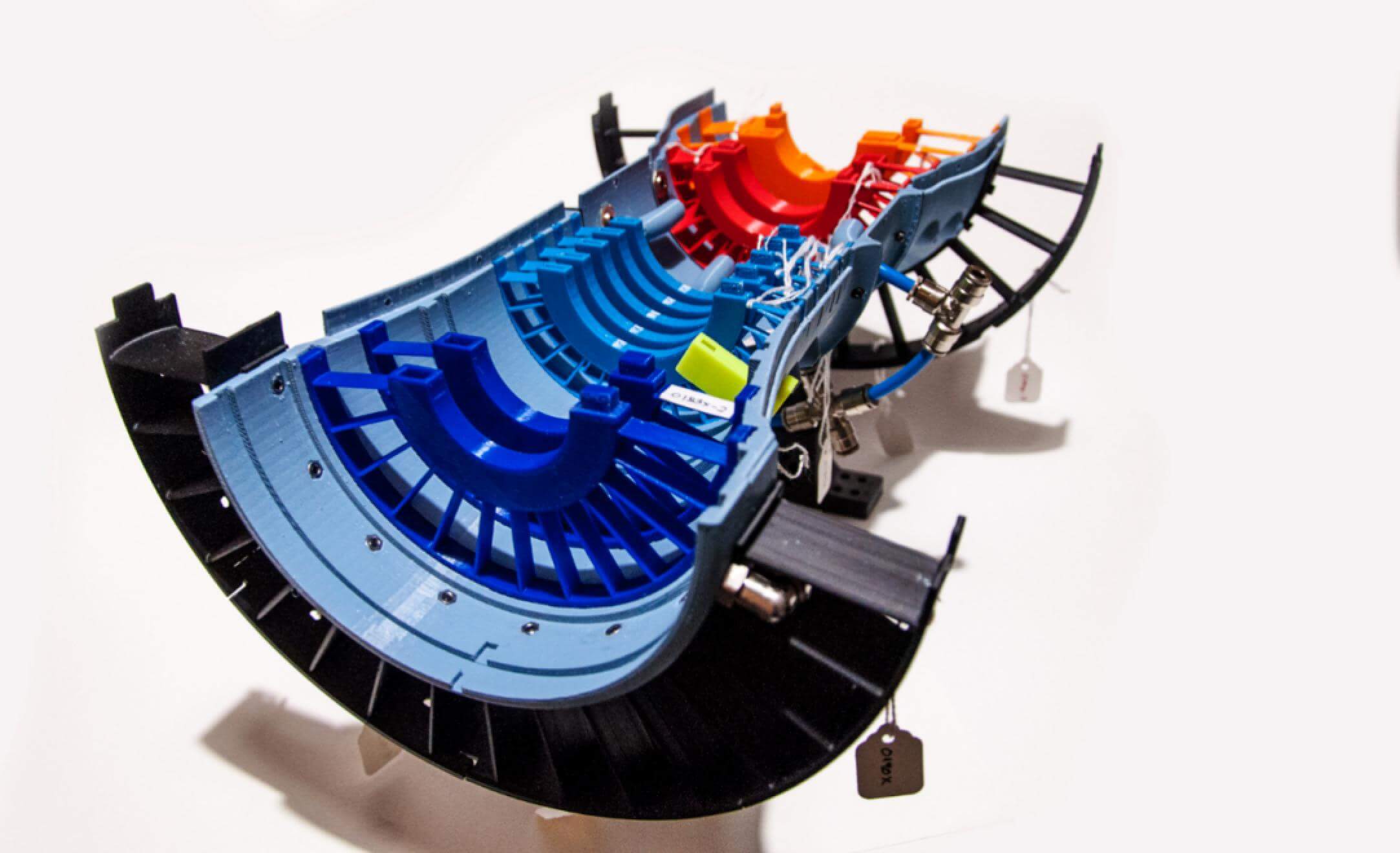
1.3, Why we Focus on the R&D of FDM and LCD 3D printers
We have highlighted what 3D printing entails, the 3D printing equipment available and how they operate. As you might have already guessed, we a 3D printing equipment manufacturing company dealing mainly in the design, creation and supply of industrial FDM 3D printers and LCD resin 3D printers.
Visiting our catalog would expose you to multiple variants of LCD and FDM printing equipment. However, before finalizing your decision on whether or not to explore our catalog, let’s lay a little emphasis on why we built our R&D process around the design and creation of FDM and LCD printing equipment.
At Dreambot3D, helping our customers make reputable decisions is our watchword. LCD resin 3D printers and industrial FDM 3D printers are the two most notable printing equipment available.
LCD 3D printing equipment is known as the best printer for individuals on a budget. They are simple to set up and gives you the confidence to design new models.
On the other hand, industrial FDM 3D printers are the mainstream 3D printers in multiple sectors. They drive filament easily and efficiently, provide prints not susceptible to fails and help reduce the long hours of tinkering and turning.
While an LCD or FDM 3D printing equipment can help keep your production line running efficiently, you might want to bear in mind that having both comes with added advantages—more on the durability LCD resin 3D printers and industrial FDM 3D printers add to the production line in chapter 3—for now, we recommend you pick a 3D printing equipment of choice from our catalog.
How to Choose the Right 3D Printer
We believe that at this point you are well informed about what it’s like to own or print with a 3D printing equipment, the best models available and why our R&D team focus on LCD and FDM 3D printers, its high time we discussed what the buying process entails.
Buying a 3D printing equipment is a low-value purchase that does not require days or week of consideration. Just like a smartphone, you can make an instant pick, build your buying decision based on the track record of a brand or focus on the needs of your production line.
Regardless of what you want to centre your LCD resin 3D printer or industrial FDM 3D printer buying decision upon, there are some key factors you must first put into consideration before visiting any manufacturers collection.
2.1, Choose 3D printer by Material
The material you want to print on determines the type of 3D printer you should prioritise. As you already know, FMD and LCD 3D printing equipment are not suitable for printing the same type of materials. LCD resin 3D printers are suitable for printing resins while industrial FDM 3D printers are suitable for printing filaments.
A typical 3D printing process might sometimes require the user to switch materials during design. This might not be termed the day to day experience of a hobbyist or even a professional in the industry, but in as far as you intend to build a career in the printing industry, it’s an experience you are going to someday have to contend with; why not prepare yourself beforehand? There are multiple FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment available, but only a few allow its user to switch back and forth between models and materials.
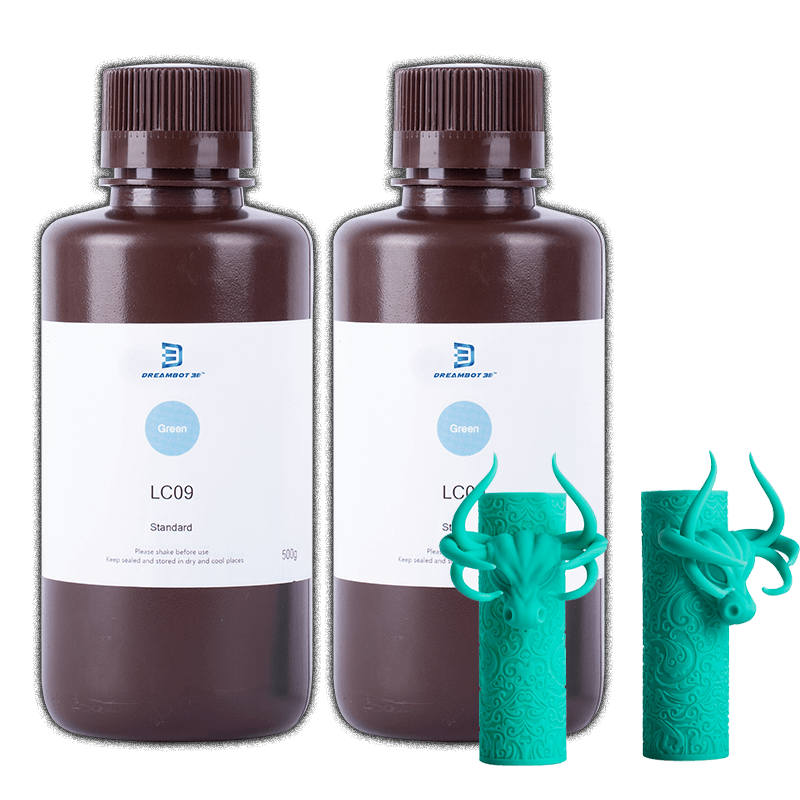

Tensile strength also plays a vital role in the printing process. Tensile strength, which is regarded as how much pressure a material can withstand before tearing apart, is also a factor to consider when looking for the best FDM or LCD machine for your printing needs.
Most filaments and resins have unique tensile strength, but when the focus is placed on the overall picture, they are not durable enough to withstand the toughness of most of the FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment available.
While there are still factors such as the melting temperature and the material’s durability to consider, their influence on the type of FDM or LCD 3D printing equipment to choose is not as consequential as the above listed.
It’s practically impossible to consider all the material you might ever have to print on using the FDM or LCD 3D printing equipment you are about to purchase, but that does not in any way means neglecting the influence of your printing material on your buying decision is probable.
3D printing can be fun and exciting and at the same time daunting and tiring; it all depends on how much time you invest in making the right buying decision.
FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment are durable modelling machines, but if due precaution is not taken during purchase, you might end up with a printer that keeps your print failing for one reason or another.
If you are looking to avoid the frustration and repetitive sequence that comes with using the wrong FDM or LCD printing equipment, we recommend you contact our support team; whether you need a low-cost 3D printer, LCD resin 3D printer, commercial 3D printer for sale, or an industrial FDM printer, Dreambot3D got you covered.
2.2, Select 3D Printer Through Application
Knowing where and how you want to use your printer can help you break down your buying decision. To help you better understand the navigational sequence behind choosing the right 3D printing machine, lets breakdown the usage of FDM and LCD printing equipment based on household, industrial and professional settings.
Household objects – These are objects you can expect to find inside your house or in an office. These items aren’t expected to endure much light or moisture exposure.
Your best option here is to use an FDM printer with Polylactic Acid (PLA), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) for filament. Print anything you expect to use with food using a food-safe filament, like PETG, coated with food-safe epoxy.
Tools – When it comes to printing tools, it really depends on where the application is. With enough infill, ABS print on an FDM printer can be really substantial. But if you need something in a professional setting, an FDM printer might not cut it.
Professional products – Manufacturers often take advantage of 3D printing to create original components. You can find 3D-printed objects in a wide variety of industries—from automotive and aerospace to dentistry. It’s more common to find LCD resin printers in a professional setting.
Note that while LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment are built to serve individuals in dynamic industries, the operation sequence, resolution, and the result of numerous variants of are different.
2.3, By Printing Size
You now the material and the application industry; it’s time to consider the print size. LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment come in multiple variants. Some are suitable for large printing tasks, while others possess printing molds that can cater to only small tasks.
How big is your business, and what size of prints do your customers demand from you regularly? At Dreambot3D, we have seen the irregularities and extra expenses that come with purchasing an LCD 3D printer that’s not compatible with the print size.
Over the years we have been in business, we have had the opportunity of interacting with consumers from different countries and region. One of the most highly influential factors most hobbyist or professionals who have walked through our door to purchase an industrial 3D printer ignore is the size of the print.
Yeah, it’s practically impossible to determine the exact size or specification attributed, or that would be required in most of the prints you make—especially if you are a business owner looking to satisfy the needs of clients from different parts of the world—but totally ignoring the print size an industrial 3D printing equipment can create is unacceptable.
LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment garnered renowned usage ahead of SLA and DLP not just because of their printing speed or the remarkable finish product they are capable of providing, but also because of their ability to perfectly create sustainable 3D models on wide materials.
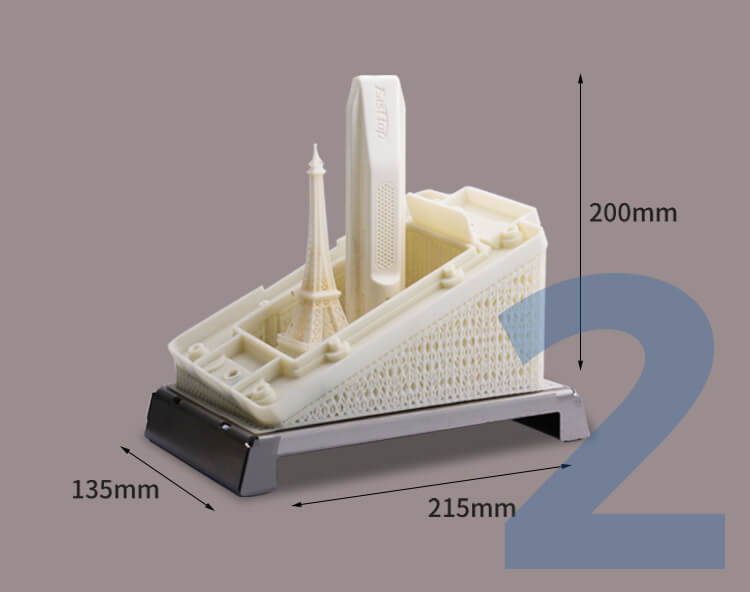
Before buying any LCD or FDM industrial 3D printing equipment, try to know the type of resin or filament it can print on and whether it’s durable enough to print perfect models on wide materials without leaving distorted edges.
The material you chose for your printing task has a lot to say about the printing size. The dimension, weight, and size of the object obtained from a 3D model printed with PLA are quite different from the result you would obtain using an ABS material—regardless of whether the CAD file and design are the same.
Considering the type of materials you would print on regularly can help you pinpoint an FDM or LCD 3D printing equipment that wouldn’t create constraints in your design’s dimension, weight, and size.
How to Combine FDM and LCD to Better Realise the Application of Printer
With the information you have about how LCD and FDM printers work, its high time we talked about how to combine both in your production line.
LCD resin 3D printers are available printing machines for creating models and patterns out of liquid resins. On the other hand, industrial FDM printers are suitable for creating patterns and models using filament.
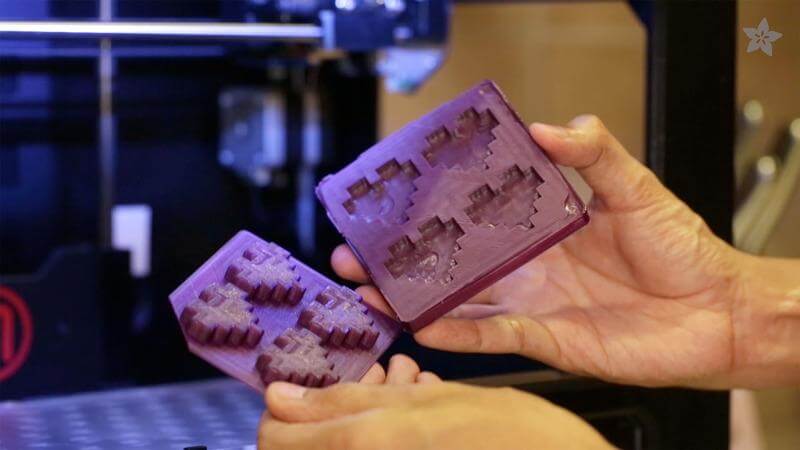

Resins and filaments are the two most common materials used in 3D printing, and LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment are the most viable machines for creating models out of both material.
Having an LCD resin 3D printer and an industrial FDM 3D printer in your production line would enable you to cater to the needs of diverse individuals from different walks of life.
At Dreambot3D, we possess 3D printing equipment that can help you better enjoy the flexible and convenient printing experience 3D printers are meant to provide. A visit to our store would expose you to LCD, and FDM 3D printers optimised to help you design more intricate and detailed models.
3.1, Why do You Need Both FDM and LCD at the Same Time
We have been talking about how important FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers are to the design and creation of efficient models. It’s obvious that many professionals and experts would be sceptical about investing in LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment at this same.
While these scepticisms can stand true for individuals catering to a specific client base, same can’t be said for production lines trying to keep up with the diverse needs of individuals from different walks of life.
FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers can help heighten efficiency and hasten the creation process in an unimaginable way. Here are some of the benefits of having both 3D printing equipment in your production line.
Dynamic Modelling Sequence: 3D printing equipment which uses FDM Technology construct objects layer by layer from the very bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament.
The whole process is somewhat similar to stereolithography. Specialized programs or Slicers “cut” CAD models into layers and computes the manner printer’s extruder would assemble each layer.
While LCD resin 3D printers display image by sending light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters. This dichroic filter separates light into three polysilicon panels.
In simple terms, a liquid 3D printer uses an array of UV LCD as its light source. The printer shines light directly from the flat LCD panel in a parallel fashion onto the build area.
Remarkable Features: With both commercial 3D printers, you get to enjoy a printing process built on flexibility, durability and efficiency.
Industrial FDM printers support operational sequences that boost your confidence to try out new models and create fun and useful things all through a custom button that easily loads and unloads filament.
LCD resin 3D resin printers are semi assembling systems not susceptible to print fails; that’s you can enjoy around the clock printing operation with this industrial FDM printers.
Suitable for Professional, Industrial and Household Setting: while LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment are optimised to cater to the dynamic needs of individuals in different industries, their reliability only goes as far as their 3D printer components can offer.
FDM printers are not reputable enough to provide the smooth finish LCD provides in a commercial setting the same way; LCD resin 3D printers are not durable enough to serve as in a household setting. Together, FDM and LCD 3D printers can help you enjoyed all-round sustained printing solutions.
3.2, What Resources can Be Saved for You by Combining FDM and LCD
Since you now know why you need FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment, it’s no news that you might be wondering what you would gain from having LCD and FDM 3D printer in your production line; that’s what resources can you save from running a production line where FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment take precedence.
Time: time as you already know is not just money, time is everything. More time means more opportunities, more production, more output, more relevance, simply put, more time begets more room for growth.
Now, in an industry where every professional and hobbyist is looking to put their best foot forward, smart works must be backed by hard work.
With an FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment at your disposal, you get to enjoy a whole new level of productivity. You can take on your daily task rest assured your mode of operation is solidly backed by machines guaranteed to provide the best possible output.
So, whether you a are a hobbyist who fell in love with the simple yet artistic thrill of 3D printing, or you are a professional who wants to heighten his or her daily input to a considerable level, having LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment at your disposal would go a long way.
Material: the difference in printing material is a common trend in the printing industry. Not all resins can possess the durability needed to print specific household items the same way not all filaments can handle the high temperature needed in printing 3D models in the medical industry.
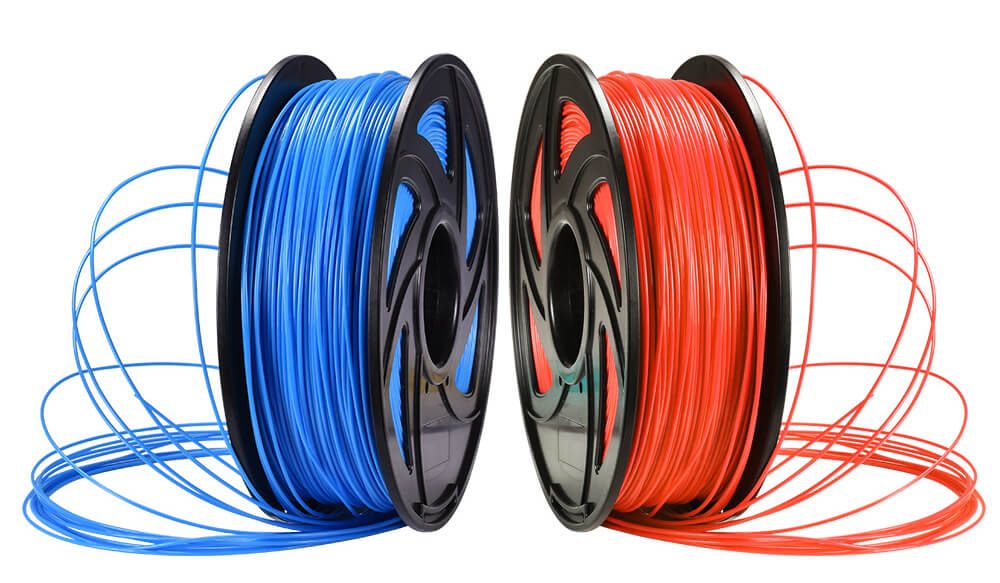

With FDM and LCD 3D printers at your disposal, you get to print on Standard thermoplastics, such as ABS, PLA, and their various blends and Varieties of resin (thermosetting plastics). Standard, engineering (ABS-like, PP-like, flexible, heat-resistant), castable, dental, and medical (biocompatible).
As a hobbyist or professional in the industry, the only way to obtain the balance needed to provide all-round satisfaction to clients is by operating with machines capable of meeting their dynamic needs on both ends.
With an FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment, this simple yet highly valued goal becomes possible. LCD printers provide the flexibility needed to print resins while FDM is notable for its ability to create remarkable 3D models out of filaments.
Money: it might not always be about profit, but it’s always about the money. Most of your day to day workload is built around satisfying the dynamic needs of your clients so they can pump in funds that keep the production line functional and your family well-fed.
With an FDM or LCD 3D printing equipment, there is no doubt that you would be able to obtain the funds needed to keep your production line functional, but with regards to the inflow and outflow of funds, you will easily come across limiting barriers.
At Dreambot3D, we optimised all our LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers to help our clients keep the production line running all year long.
If you have finalised your decision to inculcate LCD and FDM 3D commercial 3D printers into your production line or you prefer specializing in modelling filament over resin or resin over filament, Dreambot3D got you covered; get in touch today and we will have an FDM or LCD 3D printer of choice shipped to your doorstep within 3 to 5 business days.
3.3, Combining FDM and LCD Case Reference
Combining FDM and LCD 3D printer is the fastest way to heighten productivity, print in different orientations and enjoy the excellence tolerance that comes with 3D printing.
To further demystify the endless potentials and opportunities having LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers in your production line offers, let’s look at the proficiency you get to enjoy from using LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers.
Work Flow and Ease of Use: The workflow for both FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment consist of three steps: designing, 3D printing, and post-processing. First, use any CAD software or 3D scan data to design a model, and export it in a 3D printable file format.
Once the 3D printing process begins, most 3D printers can run unattended, even overnight, until the print is complete. Both FDM and LCD 3D printing equipment use support structures to facilitate 3D printing more complex geometries, and their removal represents the last step in post-processing.
Precision and Accuracy: industrial FDM 3D printers form layers by depositing lines of molten material. With this process, the resolution of the part is defined by the size of the extrusion nozzle, and there are voids in between the rounded lines as the nozzle deposits them.
As a result, layers may not fully adhere to one another, layers are generally clearly visible on the surface, and the process lacks the ability to reproduce intricate details that other technologies can offer.
In LCD 3D printing, liquid resin is cured by a highly-precise laser to form each layer, which can achieve much finer details and is more reliable to repeatedly achieve high-quality results. As a result, LCD 3D printing is known for its fine features, smooth surface finish, ultimate part precision, and accuracy.

How to Buy a Suitable 3D Printer
Knowing how to choose the right 3D printing equipment is one thing, buying a suitable 3D printer is another.
As far as you have a detailed idea of what you want from a 3D printer and understand the dos and don’ts of the 3D printing industry, buying a suitable 3D printer shouldn’t be a problem.
However, to ensure that you make the best possible decision when finalizing your 3D printing equipment purchase, let’s look at some basic factors to keep in mind.
4.1 Choose a Reliable Brand
When purchasing an LCD resin 3D printer or an industrial FDM printer, it’s important to get it from a reliable brand; it has built its name purely on quality and durability.
There are many printing brands in the market currently, and very few are reputable. 3D printing equipment are quite expensive and require a huge investment; it’s not advisable you buy from any brand. Make sure to check the brand records, reviews, and testimonials of the previous clients.
In this era, there are so many big names in the printing industry that have poor commodities. Most of these brands established their reputation in the 90s. The technological changes are so rapid that keeping up has become a problem.
While researching a brand name is important, don’t do this until you are certain you have found a formidable 3D printing equipment in their collection or you might end up wasting carrying out unnecessary research.
Counter-check if all the features listed in their LCD or FDM 3D printers are compatible with your requirements. You can use the reviews from other clients to know if the features listed are present on the actual machine.
4.2 Safety Configuration of the Machine
By now, you have made up your mind on the LCD 3D printer or industrial FDM 3D printer you want to purchase. You have set your needs and that of your client base ahead of budget, and you are all good to make payment; Wait! one more thing.
What’s the safety configuration of the machine-like? Hope you are not about to purchase a ticking time bomb? 3D printing equipment safety configuration can look complex, especially during rough situations.
Explore the dos and don’ts of the machine’s safety configuration, know where and where not to press in case of overheating, and above all, make sure your purchase is backed with an instructional guide.
Most reliable 3D printing equipment manufacturer provides support to enable you to navigate your way around the 3D printing equipment before finalizing your purchase.
However, if such services are not provided by your preferred LCD or FDM manufacturer, use the instructional manual provided to explore the safety configuration before finalizing your purchase.
If you are of the notion that this process is quite complex and require assistance understanding the intricacies involved, we recommend you visit our 3D printing equipment catalog; our support team would guide you through the buying process.
4.3 Resolution Requirement of the Machine
Most 3D printing are built to ensure consistent temperature throughout the building process, but not all can give you the surface finish you desire. LCD 3D printers and industrial FDM 3D printers vary based on resolution, shape and size, and the pricing and buying process are hugely dependent on these features.
While it’s nice to have an LCD and FDM 3D printing equipment with high screen resolution in your production line, note that these printers are quite expensive and sometimes these machines are viewed as wants instead of needs—that’s quite luxurious but not necessary.
To be on the safe end, try to vet the resolution requirement of wax 3D machines needed to run your production line efficiently. Knowing the resolution requirement of your machine can help you save cost and land the most lucrative 3D printing deal for your printing needs.
Note that the need to obtain a high-resolution 3D printing equipment cannot be overemphasized. A production line equipped with low-resolution 3D printers doesn’t just hinder efficiency; it also drives customers away.
Whether you are a hobbyist looking for the best FDM 3D printer for home use or a professional looking to obtain the best deal on LCD resin 3D printers, endeavour to place due attention on the resolution requirement of the machine you are about to purchase.
4.4 Consider Whether the Price of the Machine is Acceptable
You can find 3D Printers for under $1000. Most of those are 3D printing equipment have very small build surfaces and other limitations.
Occasionally a gem is found though in that price range, so it is worth doing the research on the cheaper printers. Keep in mind though that with cheap, you get what you pay for.
That 3D printing equipment may need a lot of extras or add-ons to make it reliable or high enough quality. At which point it might be better to spend more on a better printer in the first place.
At the moment, a good starting printer can be found for around $300. These would be kits that need to be assembled. Out of the box, ready printers begin at around $800 but are routinely seen in the $2000 — $5000 range.
One kilogram of plastic filament sells for $20 — $200, depending on the filament type and vendor. PLA/PLA+ is a good general use plastic which is at the bottom end of that price scale (and recommended for starting out with).
ABS or PETG would be a better choice for high-temperature applications (like sitting in the sun, or in a car in the sun) and sell for $35 and up for a kilogram.
It might be considered a good practice to have a collection of replacement parts for just about everything the printer needs. A spare extruder, control board, power supply display screen, wires, rods, etc.
If any of these items need to be replaced your printer is most likely unusable until the replacement arrives. Having that replacement on hand reduces your downtime. This is not “required”, but commonly recommended.
Before you dive into conclusions as to the LCD resin 3D printer or the industrial FDM 3D printer to purchase, make sure you have a proper estimate of the funds you can invest in the buying process.
A 3D printer manufacturer’s support team would be able to guide you better if you can provide a rough estimate of the price range you expect your desired 3D printing equipment to be within.
4.5 Consider the Suppliers After-sales Service Capability
Many folks place all their focus on the remarkable features a machine offers and forget to obtain detailed info on what their suppliers after service capability is like.
From experience, we can boldly tell you that a remarkable LCD resin 3D printer or an industrial FDM 3D printer with no warranty policy guiding its purchase would do you more harm than good.
Every reliable 3D printing equipment supplier attributes a warranty policy of not less than one year to each product available in its collection. If you are about to purchase a 3D printer and a warranty policy of less than one year is thrown your way, abort purchase.
Also, take note of technical support. 24 hours support service is ideal. However, there are a lot of formidable companies not offering round the clock support. Before finalizing your purchase, try to ensure that the brand you are banking with possesses technical support with a viable track record.
4.6 Consider the Service Life of the Machine
The service life for most 3D printing equipment is about 5 to 10 years. While the warranty policy on most 3D printers doesn’t grant you access to refunds or after-sales privileges 1 or 2 years after purchase, purchasing a 3D printing equipment from a reliable manufacturer comes with the guarantee that your machine will be in shape and keep your production line running for at least five years.
With that being said, it’s important to note that the estimated service life of the machine can change at any time based on external factors.
How you use your machine determines how long it would last. If you leave you industrial FDM 3D printer or LCD resin 3D printer packed dirty on a regular, you shouldn’t expect the ten years life expectancy to hold any ground.
If you went gone through the hassle of finding the right 3D printing equipment from a reliable brand, inspecting all the necessary features and finalizing the purchase, you wouldn’t want the whole effort you put in to go down the drain based on negligence from your part.
If you try as much as possible to keep your 3D printing equipment clean and in good shape, service life expectancy wouldn’t be an issue.
4.7 Consider the Maintenance Cost of the Machine
3D Printing equipment is not as fast as the Star Trek Replicator devices. It takes time to build a 3D object. Smaller objects can be created in 15 minutes or so, but larger objects can take many hours or even days to print.
Some printers are faster than others. That speed though is a result of the individual 3D Printer design and how the printer is tuned.
The maintenance cost of a 3D printer is not huge. However, this cost will be determined by where you’ll be using the machine.
Using 3D printing equipment to print for hours can cause some mechanical parts to lose its grip or hold to the machine; some might degrade after months of being used. If not upgraded, the final quality of your prints will consequently reduce.
Therefore, machine maintenance is necessary, and it might come with added costs where some parts like the nozzle may need to be replaced entirely. You must incur a reasonable maintenance cost of your machine to consistently get clean and fine detailed prints.
Dreambot3D is a 3D printer manufacturer that defied the odds by manufacturing machines that are highly versatile, cost-effective, easy to use and maintain, while still giving you high detail prints.
If you are interested in finding out which 3D printing equipment is best suited for your needs, get in touch with our support team today.
Conclusion
LCD resin 3D printers and Industrial FDM 3D are two distinct 3D printing equipment capable of handling all the dynamic and intricate task involved in the printing process.
These 3D printers come in different variants and models and are termed suitable for every production line.
However, while LCD 3D printers are suitable for printing resins and FDM 3D printers for creating models using filaments, both 3D printing equipment can serve as viable tools in boosting efficiency, reliability and durability.
If you are serving a client base made up of individuals from all walks of life, we recommend you have both machines in your production line.
With all the information we detailed above, we believe you are well equipped with everything you need to make the right buying decision when scouring through catalogs to find the best 3D printing equipment for your production line.
Dreambot3D is a 3D printing equipment manufacturer dealing mainly in the design, development and distribution of LCD resin 3D machines and industrial FDM 3D printers.
If you are in search of cost-efficient 3D printers with excellent tolerance, a nozzle that heats up almost immediately, and lifetime technical assistance, don’t hesitate to get in touch.
FAQ Guide
Is LCD better than DLP?
Both DLP and LCD are used in the dental, jewelry and engineering industries, just to mention a few. Naturally, there are also a fair number of hobbyists using both types of printers. Looking at the market, the general trend is that DLP printers are the more expensive, professional machines. LCD, a more recent technology, has so far been seen mostly in affordable, desktop printers. Cheaper DLP printers sometimes suffer from minor voxel distortion. However, that potential issue becomes less of a problem if one invests a little more money. That’s because, with higher quality printers comes higher quality hardware, which is designed to correct for distortion. In general, LCD 3D printers use cheaper components than DLP 3D printers, making them a cheaper resin 3D printing solution. This is a great thing because it extends the reach of resin 3D printing to a wider audience of makers.
Is LCD stronger than DLP?
Yes, LCD 3D printers are way stronger than DLP printers. There is no DLP 3D printer on the market today comparable in strength and mechanical performance to LCD 3D printers. DLP 3D printing resins typically cost more and yield less parts per resin unit than LCD 3D resin printing does.
How do resin 3D printers work?
The machines for resin-based 3D printing use neither powder nor filament; they use liquid resin. The resin 3D printing process takes place in a large tank and begins with a layer of liquid polymer spread over a platform. Since this piqued polymer is UV-sensitive, a UV laser hardens the area that will become one layer of your 3D print. The rest of the layer stays liquid. The platform is then lowered and the next layer is drawn directly on top of the previous one. When the object is complete, it is raised out of the tank via the supporting platform – much like a submarine rising to the surface of the water – with the excess liquid flowing away. Because a liquid material is used (and not powder), you need to add support material for overhanging parts and parts that stick out. The supports will then be removed manually after the model is taken from the machine. This means that the design freedom of this technology is somewhat limited. The main advantages of materials printed with resin 3D printers are smooth surfaces and a lot of finishing and post-processing possibilities. Materials used in this printing process include standard resin, mammoth resin, transparent resin, and gray resin. They all feature smooth, high-quality surfaces.
Can you 3D print liquid?
Yes, you can 3D print liquid. It sounds bizarre, but it’s true. Researchers at the US Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory developed a way to 3D print liquid using modified conventional 3D printing equipment. This equipment supports the printing of stable liquid structure. That’s for you to 3D print liquid; the liquid must be in a fixed and stable containment. Note that 3D printing liquid is quite complex; if you are not familiar with the regular printing procedures, it’s best you seek expert advice from a professional before embarking on the task.
Are resin printers faster than FDM?
Yes, resin 3D printers are faster than FDM. LCD 3D printers form or create objects by surface while FDM 3D printers form objects by dots. When working with larger plane, resin 3D printers tend to be faster than FDM.
How difficult is it to learn 3D printing?
It’s not difficult to learn, just an overwhelming number of things that you’d need to learn. But if you’re good at math then it’s not that difficult. Or if you’re good at sculpting or carpentry and stuff. If you can build Ikea furniture without a manual and within an hour then you should be able to understand the concept of 3D… Still, the whole 3D printing world is a simplified version of Computer-aided design/Computer-aided manufacturing where the CAD is you modelling a model in 3D with software and the CAM is sending the model to the 3D printer for the final result. Both techniques are decades old already but are now brought to the masses through 3D printing. The CAM part of 3D printing is hardware dependent. You generally need a 3D printer that uses one of the many techniques to make a 3D model from filament, resin or other materials. But you can also use a CNC machine where the machine basically cuts away parts that are not part of the model.
How expensive is 3D resin?
3D printing is an expensive venture. Before diving into it, weighing the cost of the basic materials required is essential. The cost of a 3D resin varies based on geographical location, type of resin and the quantity required. Nowadays, the standard price for a 1-litre water bottle of liquid resin is around $50. This price is for a very low-end resin product. For professionals who want to get the best quality possible, a premium resin could cost as much as $500 per litter.
What happens if you touch uncured resin?
Depends; some people will have allergic reactions, while other would easily go scot free with no reactions at all. Direct contact is not recommended, and according to professional requirements, its advised you put on gloves during operation. With the right equipment and tools, you can easily work with uncured resins without fear of getting hurt.
How strong is 3D printed resin?
The durability of a 3D printer resin is measured based on its tensile strength. The standard 3D printer resins are not as tough as most of the materials used by FDM printers. However, just because the resin is tough, it doesn’t mean that prints made from these resins will be twice as strong than if printed with a standard resin. Other factors, like model design and print settings, play important roles in the final print’s strength. Nonetheless, comparing tensile strength is a straightforward way to determine which material is stronger.
What is a thermal wax printer?
Thermal wax printers use heated pins to ‘burn’ images onto heat-sensitive paper. These printers are commonly used in calculators and fax machines; and although they are inexpensive and print relatively fast, they produce low-resolution print jobs. Thermal wax printers use thermal wax ribbon to melt coloured wax on paper for a photo print. Jack Kilby invented it.
Can you use candle wax for lost wax casting?
Derived from petroleum, this is one of the most common waxes used by lost wax casting jewelry sculptors. It is also derived from petroleum and is commonly used in candles. It’s not ideal for hand modelling jewelry, but it can be used as an additive to other waxes to make them slightly harder.
What should I know before buying a 3D printer?
There are a lot of factors to put into consideration when buying a 3D printer. First things first, you might want to take note of what you need the 3D printer for. Are you into commercial 3D printing, or are you a hobbyist looking to design personalized models? If you are looking for a 3D printer to satisfy your personalized 3D printing needs, you need not worry much about your buying decision; detailing out the features and specifications you require from the machine would do the job. But if you are looking to fill a market need and need a 3D printer for the job, put the following factors into consideration; who is my target audience? Do I need a filament or resin 3D printer to fulfill my customer’s needs? What specification and features do I need from a preferred 3D printer? What’s my budget like? To get detailed info on all the factors you need to consider when buying a 3D printer, please refer back to chapter 4 of Dreambot3D’s LCD 3D printer buying guide.
What is the difference between FFF and FDM?
There is no much difference between FFF and FDM. FFF stands for Fused Filament Fabrication and goes by a printing process that involves building an object by depositing melted material layer by layer, same as Fused Deposition Modelling FDM. The only thing differentiating the two terms is the historical background. The layer-by-layer 3D printing process was first regarded as FFF until Stratasys {a leading company in 3D printing and development} trademarked the FDM term in 1989.
What are the benefits of additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing simplifies the printing process to an extent where even the average joey can enjoy an out of the box printing experience. Additive manufacturing aids users in printing assemblies as a single piece. That’s you get to save money from every printing process. Additive manufacturing also gives users the opportunity of printing multiple movable parts as a single piece. Compared to other conventional manufacturing processes, additive manufacturing helps you enjoy a simplified yet highly accurate printing process.
How do I increase the resolution on my 3D printer?
Use the highest possible resolution settings on both the printer and the application being used. These settings can usually be adjusted from the ‘Print’ menu or on the printer’s control panel. Choose the highest dots-per-inch (dpi) setting. Depending on the device specifications, the dpi settings will range from 72 to 2400 dpi. The most fundimental way to improve the quality of the 3D print is to make sure that the bed is level and the nozzle distance is set properly. You can use a sheet of paper or feeler gauge to determine the distance between nozzle and bed. When the (clean) nozzle is the appropriate distance from the bed, the paper or gauge will have minimal resistance when pulled free. It will also go back underneath the nozzle without force. Repeat this procedure two or three times to ensure that it is accurate. The temperature of the nozzle — or nozzles, if there are more than one — directly effects the appearence of the print. If the nozzle is too hot, it could leave strings of filament between separate parts. When building tall pieces, high temperatures melt the earlier layers, resulting in malformation. When building taller prints, include a one-centimeter cube built on the opposite side of the build plate. This removes the hot nozzle from the print and allows time for cooling. If there are strings of filament between structures, use a wall or ooze shield structure, a common feature in slicer programs.
How big can a 3D printer print?
Our regular FDM 3d printer is up to 1000*1000*1000mm; if you require something larger, we can easily customise based one based on your specifications. The maximum print size of our LCD can reach 520*295*550mm.
Can 3D printers be used for mass production?
Mass production using 3D printing can greatly reduce time to market by avoiding traditional tooling methods, cutting lead times on prototypes and end-use parts. … An example is custom 3D printed molds for injection molding. For low-volume production (approximately 10-100 parts), 3D-printed molds save time and money.
What is the strongest plastic for 3D printing?
Polycarbonate is the undisputed king of materials for desktop 3D printing. Even we were surprised at polycarbonate’s strength. In comparison to nylon at 7,000 psi, polycarbonate’s tensile strength of 9,800 psi makes it the ideal choice for high-strength, functional components.
How long does it take to 3D print a car?
3D printing a car can take from 30 minutes to 7 days. When it comes to 3D printing a car, a lot of factors must be put into consideration. The first thing to consider is the individual or company’s experience catering to the printing task; if it’s a one-person job, what’s your experience or track record like? With that in mind, the CAD design, printer, resin, and other materials required for the printing process are to be considered. Note that the type of 3D printer you are using plays a vital role in determining the amount of time that would be spent or needed for the task.
Is 3D printing going to change the world?
The advancements in the hardware, software, materials and applications suggest that 3D printing will eventually become yet another manufacturing technology. Naturally, the adoption rate of 3D printing will increase over time, with some segments like dental almost entirely switching to 3D printing. The growing awareness of 3D printing and its benefits will facilitate this growth. In the meantime, the competitive 3D printing landscape will require companies to differentiate themselves from competitors by leveraging their unique expertise and developing a clear value proposition.
How strong are 3D printed parts?
3D printed parts are strong enough to be used to make common plastic items that can withstand great amounts of impact and even heat. For the most part, ABS tend to be much more durable, though it does have a much lower tensile strength than PLA.
What can you make with a 3D printer?
It’s not difficult to learn, just an overwhelming number of things that you’d need to learn. But if you’re good at math then it’s not that difficult. Or if you’re good at sculpting or carpentry and stuff. If you can build Ikea furniture without a manual and within an hour then you should be able to understand the concept of 3D… Still, the whole 3D printing world is a simplified version of Computer-aided design/Computer-aided manufacturing where the CAD is you modelling a model in 3D with software and the CAM is sending the model to the 3D printer for the final result. Both techniques are decades old already but are now brought to the masses through 3D printing. The CAM part of 3D printing is hardware dependent. You generally need a 3D printer that uses one of the many techniques to make a 3D model from filament, resin or other materials. But you can also use a CNC machine where the machine basically cuts away parts that are not part of the model.
Is PLA cancerous?
A limited study back in 2013 by researchers from the Illinois Institute of Technology and The University of Texas at Austin suggested that ABS and PLA filaments do release some unhealthy particles into the air during 3D printing, but those same researchers are now back with a more comprehensive study. And the results are not very good – when 3D printing certain filaments in confined spaces, high levels of possibly carcinogenic (cancer-causing) particles can be measured in the air. This has become apparent from a study entitled Emissions of Ultrafine Particles and Volatile Organic Compounds from Commercially Available Desktop Three-Dimensional Printers with Multiple Filaments, which has just appeared in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.